
Hyperhidrosis is a disorder in which there is excessive activity of the sweat glands, exceeding the physiological need to regulate body temperature. This condition can occur even when not exercising or in hot weather. Hyperhidrosis can occur all over the body or in certain parts of the body, such as the palms, soles, armpits and face. Hyperhidrosis can be experienced by anyone, but this condition most often occurs in the age group of children or adolescents. Although not dangerous, hyperhidrosis can cause psychological problems for sufferers, including embarrassment, stress, depression, and anxiety.
Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is characterized by sweating in an amount that exceeds normal limits without any triggers. A person can be suspected of suffering from hyperhidrosis if:
- The beads of sweat can be seen clearly when the weather is not hot or when you are relaxing (not doing much activity)
- His clothes are often wet with sweat
- Experiencing disturbances during activities, for example difficulty opening a door or holding a pen because your palms are wet with sweat
- The skin appears thin, cracked, and flaky, with a paler or reddish color
- Often experience skin infections in parts of the body that sweat too much
- Family history with the same complaint
Symptoms of hyperhidrosis can differ, depending on the type. Based on the type, hyperhidrosis consists of 2 types, namely:
- Primary hyperhidrosis
Occurs for no apparent reason, usually in one or several areas of the body, especially the armpits, hands, feet or forehead. Usually primary hyperhidrosis occurs from childhood or adolescence.
- Secondary hyperhidrosis
There are clearly identifiable causes, such as a history of drinking alcohol, hyperthyroidism, diabetes, and malignancy. It usually causes the whole body to sweat profusely, even while sleeping. Patients usually only experience secondary hyperhidrosis after adulthood.
Diagnosis of Hyperhidrosis
To make a diagnosis of hyperhidrosis, the doctor will take an history or ask questions regarding the symptoms experienced, the age at which the first symptoms appeared, as well as the patient's and family's medical history. After that, the doctor will carry out a thorough physical examination. Then, to determine the cause of hyperhidrosis, the doctor will also submit several supporting examinations, including:
- Blood and urine tests
This test is used to determine whether there are medical conditions that can cause hyperhidrosis, such as hyperthyroid disease and diabetes.
- Sweat test
This test is done to find out which parts of the body experience hyperhidrosis and its severity.
Hyperhidrosis Management
Treatment for hyperhidrosis is based on the cause. Treatment steps that doctors usually take to treat hyperhidrosis are:
- Administering topical medication
The medicine that is usually given is an antiperspirant containing aluminum chloride. This medicine is rubbed on the skin at night and must be washed off in the morning.
- Drinking medicine
Drugs that can also be used are anticholinergic groups, to inhibit the work of the nerves that trigger sweating. In addition, antidepressant class drugs can also be given to reduce sweat production and reduce anxiety which can exacerbate hyperhidrosis.
- Iontophoresis (sweat inhibition device)
This action can be done if hyperhidrosis occurs in the hands or feet. This therapy is done by immersing the patient's hands or feet in water. After that, electricity will be channeled through the water to block the sweat glands.
- Botulinum toxin injection
Botulinum toxin injections can temporarily block the nerves that cause excessive sweating. The effects of the injection can last up to 12 months and must be repeated.
- Sympathectomy surgery
Video Assisted Thoracoscopic sympathetic nerve surgery is the treatment of choice for primary upper limb hyperhidrosis with an excellent success rate . The operation was carried out using a minimally invasive method, with a small surgical wound so that there is minimal postoperative pain and minimal scarring. This is done by burning or clamping the nerves that control sweating in the hands.
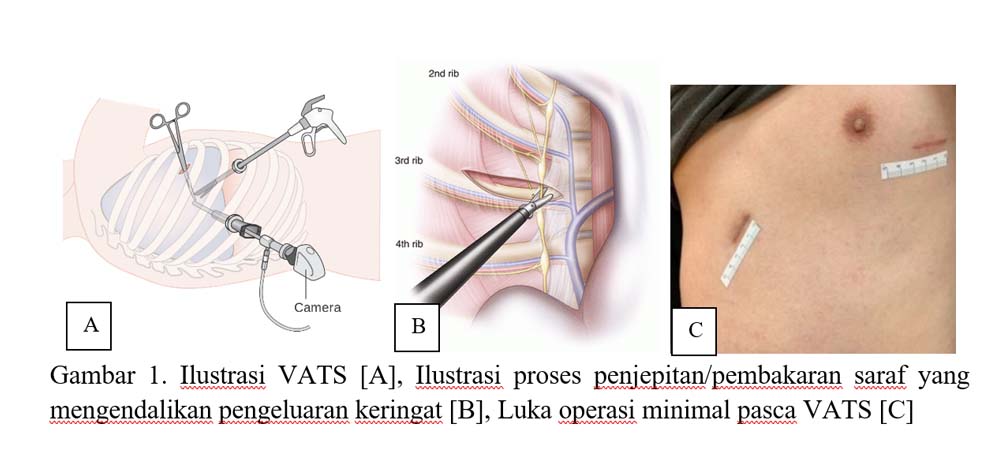
Apart from undergoing medical treatment, patients can perform self-care to control sweating and prevent body odor , such as:
- Bathe every day to prevent bacteria from growing on the skin
- Dry the body after bathing, especially the armpits and between the fingers
- Wear leather shoes and cotton socks that absorb sweat
- Change socks regularly or when they start to feel damp
- Not wearing closed footwear too often
- Choose clothing materials that are cool on the skin for daily activities and clothes that easily absorb sweat for exercising
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, to manage stress that can trigger hyperhidrosis
Article written by dr. David Hutagaol Sp.BTKV (K)-VE (Specialist in Thoracic, Cardiac and Vascular Surgery at EMC Pulomas Hospital).
