
Diabetes Mellitus or "sugar disease" is defined as an increase in blood glucose levels as a result of the body's inability to process carbohydrates or glucose due to a lack of insulin or insulin not functioning properly (insulin resistance occurs in the body). The prevalence of diabetes is increasing by a large proportion in the world. In Indonesia, the number of diabetics is estimated to increase from 8.4 million sufferers in 2000 to around 21.3 million sufferers in 2030. In 2013, Indonesia was ranked 7th in the world and is expected to rank 6th in the world in 2030 in terms of number of diabetics (ADA, 2019).
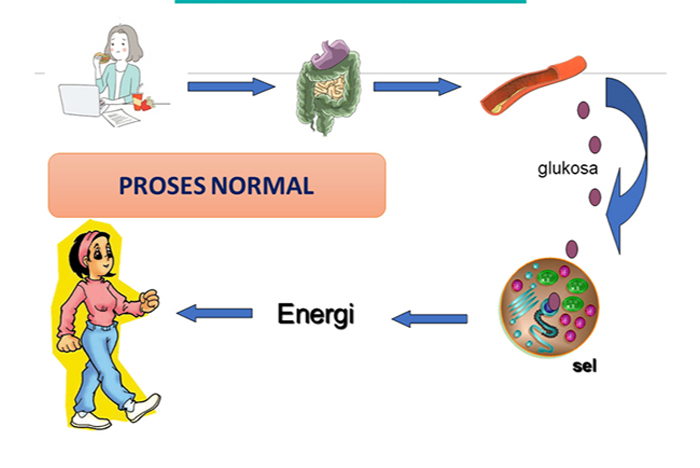
To be able to carry out daily activities, humans will need energy. Under normal circumstances, when food enters the body, the food will be metabolized in the digestive tract. Glucose will be absorbed in the intestines and circulated throughout the body through blood circulation until it reaches the cells. The entry of glucose into these cells requires insulin. After glucose enters the cell, metabolism in the cell is continued with the final result being energy. (Image 1.)
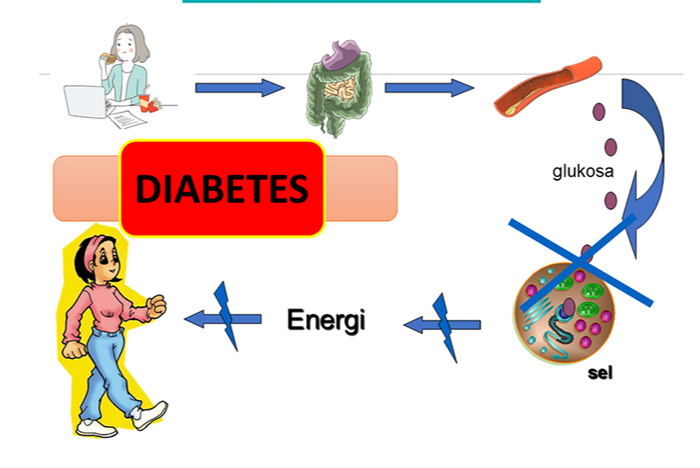
In diabetics, the metabolism of glucose into energy is disrupted. This is because glucose in the blood cannot be entered into cells, due to reduced insulin, or cells resistant to insulin. So that the amount of glucose in the blood continues to increase. (Figure 2.)
Diabetes itself is divided into several types, namely;
- type 1 diabetes; occurs due to lack of insulin produced by pancreatic beta cells. Can be caused by a viral infection, autoimmune disorder, or hereditary (causing degenerative beta cells, even in the absence of a virus or autoimmune disease)
- type 2 diabetes; is the more common type of diabetes. This type of diabetes occurs because glucose cannot enter the cells because the cells are resistant (immune) to insulin. In normal people, glucose can enter the cells easily
- type 3 diabetes; associated with Alzheimer's in old age
- Other types of diabetes: LADA, MODY
- Diabetes in pregnancy
RISK FACTORS OF DIABETES MELLITUS | |
Controllable Risk Factors | Uncontrollable Risk Factors |
o Family history of diabetes o Age o Gender
| or Obesity or high blood pressure o Cholesterol levels o Impaired glucose tolerance o Lack of movement |
The symptoms of diabetes themselves are known as classic symptoms, namely: " 5P " which consists of: Polyuria (urinating a lot), Polydipsia (drinking a lot), Polyphagia (eating a lot) , Weight loss for no apparent reason, Pruritus ( itchy rash). Other symptoms that may be felt by patients can include: blurred vision, difficult to heal wounds and tingling.
The criterion for the enforcement of diabetes mellitus is to check blood sugar levels in the capillary veins. It is said diabetes if:
- Fasting blood glucose level ≥ 126 mg/dl, or
- Blood glucose level 2 hours after eating ≥ 200 mg/dl, or
- HbA1C ≥ 6.5%
- There are classic symptoms and GDS ≥ 200 mg/dL
Diabetes mellitus cannot be cured, but can be well controlled. Treatment of diabetes is known by using 4 pillars, namely:
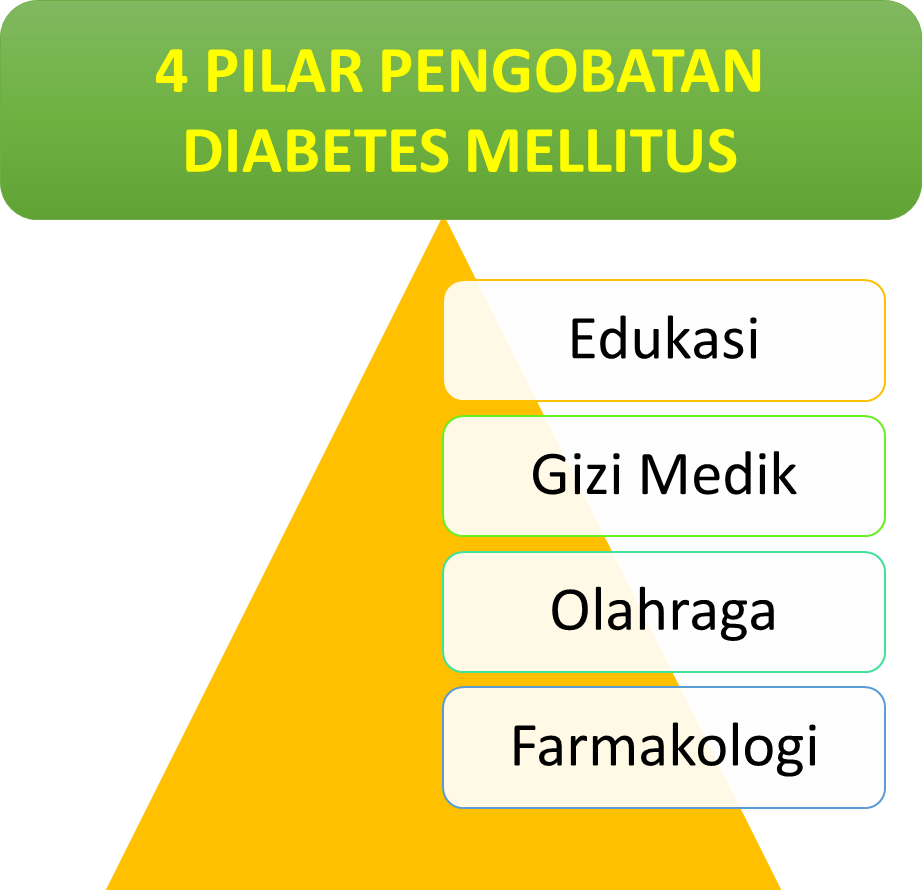
4 pillars in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus:
- Education: Knowledge about Diabetes Mellitus, starting from the types of diabetes, lifestyle and eating patterns that can cause diabetes, to knowledge about self-monitoring of blood glucose.
- Medical Nutrition : A balanced nutritional intake is necessary for the management of diabetes mellitus. The recommended carbohydrates are 45% - 65% of total energy intake. Fat intake is recommended around 20% - 25% of calorie needs. The recommended protein is 10% - 20% of the total daily energy intake. However, these nutritional needs are readjusted if there are complications in the patient.
- Sports: Busy daily activities often make you forget about sports. However, exercise is very important to help cure diabetes mellitus patients. Avoid lazy activities such as watching TV, using the internet for a long time, playing computer games, and so on.
- Pharmacology : Sometimes a healthy lifestyle is not necessarily enough to control blood glucose levels. Therefore doctors usually prescribe certain medications to help lower glucose levels back to normal.
Checking blood sugar regularly is important to know your health condition. There is no need to wait for certain symptoms, because diabetic patients often do not realize that they have diabetes. According to WHO, sugar consumption should be limited to <50 grams per day. Sugar intake needs to be controlled, because apart from causing diabetes, it can also:
- Increases blood pressure
- Increase body fat
- Increase cholesterol & other fats in the blood
- Increased chance of cardiovascular disease
If not properly controlled, diabetes can cause the following complications:
- Microvascular complications (small blood vessels)
- Neuropathy (peripheral nerve damage)
- Retinopathy (eye nerve damage)
- Nephropathy (kidney damage)
- Macrovascular complications (large blood vessels)
- Coronary artery disease (coronary artery disease of the heart)
- Peripheral artery disease
- Strokes
Diabetic foot disease is one of the most common complications found in people with uncontrolled diabetes. Peripheral nerve damage is the main cause of this diabetic foot which can eventually develop into a diabetic ulcer and even end in amputation. Periodic control, use of proper footwear to prevent foot deformity, avoid injury is one of the things that must be done in preventing diabetic foot disease.
This article was written by dr. Apriliana Adyaksari, Sp. PD, M. Kes (Internal Medicine Specialist at EMC Hospital Tangerang). Dr. Apriliana's practice schedule at Tangerang EMC Hospital: Monday, Wednesday, Friday (07.30 – 14.00), Tuesday & Thursday (13.00 – 20.30), and Saturday (08.00 – 13.30).
